The Differences Between Options and Futures
Date Modified: 3/23/2023
Both Options and Futures are types of derivative products that are widely traded in the US and provide traders with access to a plethora of financial markets. In addition, both can be used to hedge risk and speculate on price changes. However, it is important to keep in mind that these two types of derivative contracts differ from one another. Here’s what you need to know about Options vs. Futures trading:

What Are Options?
An Options contract is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price and date. Option sellers have the corresponding obligation to sell or buy an asset, depending on where the underlying future settles. As mentioned above, Options are multifaceted and allow traders access to multiple financial markets that range from stocks to commodities and currencies to indices and more.
Types of Options
There are two types of options that traders should familiarize themselves with; a Call Option and a Put Option.
Call Option
Simply put, Call Options give the buyer the right to buy an underlying asset at a specified price, prior to or at the expiration of the option. It is common to use call options to speculate on potential price increases of an underlying asset.
Put Options
Put Options grant buyers the right to sell the underlying asset before or at the expiration date. In most cases, Put Options are used to protect against a potential decline in the value of an underlying asset.
Futures Contracts Explained
Futures contracts are derivative contracts that are established between a buyer and a seller, in order to transact a financial asset at a preset price and time in the future.
Another way of putting it is that two parties enter into an agreement whereby one of them will buy the underlying asset of a Future, and the other will sell it at a specific price and time in the future, regardless of the prevailing market price at the time the contract is established. To find out more about Futures contracts and how you can trade them, read our article on how to trade Futures contracts.
Similarities Between Futures and Options
Some of the similarities between Options and Futures include the fact that these are both derivative contracts, meaning that their value is derived from the underlying asset. In addition, both Futures and Options have expiration dates and both contracts allow traders and investors access to a wide range of markets all while speculating on the underlying asset’s price and potentially using these products to hedge on risk.
Key Differences Between Futures and Options
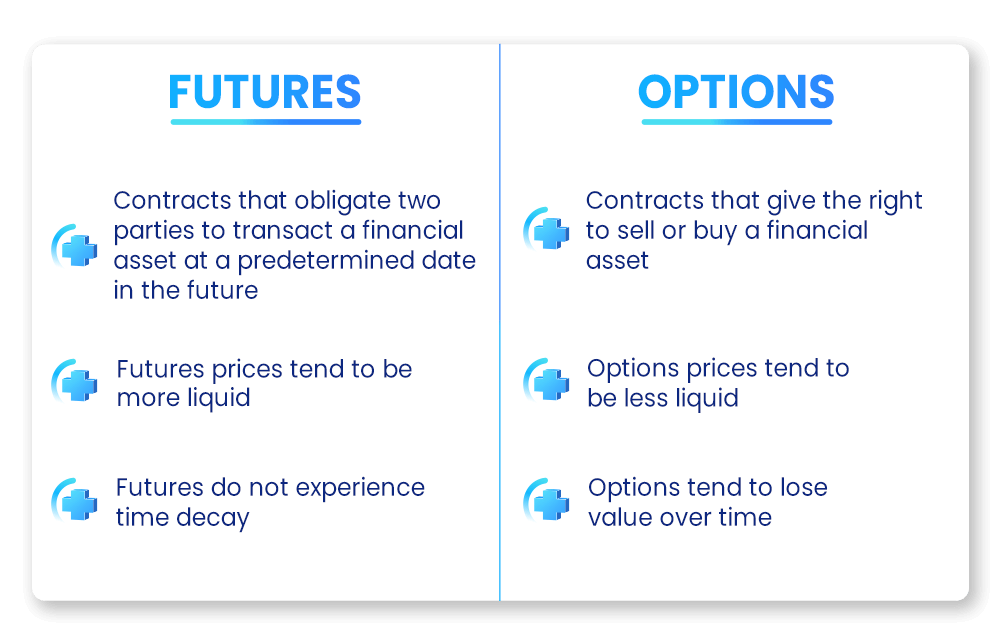
When comparing Options vs. Futures it is important to keep in mind the differences between them. One of the most prominent differences between Futures trading and Options trading is perhaps the fact that Futures contracts obligate the buyers and sellers to buy or sell the Futures’ underlying assets at a predetermined place and time in the future. On the other hand, long Options are not an obligation but rather a right to buy or sell the underlying asset in the future.
Furthermore, the Futures' expiration date is typically longer than the Options’ expiration. This is because whereas Options often expire after a year or less, Futures’ expiration can vary from days to months and multiple years, hence making them more suitable for long-term investors.
Margins and Premiums
Both futures and options have requirements that must be adhered to in order to sustain an open position. These requirements are called margins and premiums and are upfront payments that must be covered by the potential traders. The difference between margins and premiums goes as such:
Margin is a withholding required by the exchange for Futures contracts to ensure that the buyer or seller can fulfill their obligations. This margin covers potential losses if the asset prices move against the buyer or seller. It is usually a percentage of the contract value. In short, margins represent a fraction of the total value of a futures contract. To find out more check out our article about Futures margins.
On the other hand, Options contracts have what’s called a ‘premium.’ This is the price paid by the buyer for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at the specified time and price and is affected by various factors, based on the underlying asset's market value, the Options’ expiration date, and market volatility. If an option is not exercised, the buyer loses this premium and the seller collects it. Over time, this premium will decay, leading to potential losses for the buyer even if the underlying future moves in the option’s favor.
Futures vs Options: In Conclusion
Both Futures contracts and Options contracts allow access to rich and multiple financial markets. Nonetheless, each type of trading has its own pros and cons, and traders and investors interested in one or the other need to take into account the differences mentioned above in order to determine the best type of trading for them. If Futures trading speaks to you and caters to your needs, Plus500 offers Futures contracts on Forex, Indices, Cryptocurrencies, Commodities, and more.
